Non-destructive Examination / General Examination
KNDE will become a company prioritizing people and nature.
Radiographic Test(RT)
- Basic principle
- Detecting any fault on the film from the concentration difference of amount of irradiated radiation at the sound area and faulty area, or changes with strength of irradiated radiation when it was shot at the test subject
- Subject and application
- Detecting any fault on the inside or outside of a welded part or cast part
- Features
-
- - Semi-permanent records
- - Applicable to almost any material
- - Capable of detecting any fault on the surface or inside
- - Requires radiation safety management

Ultrasonic flaw detecting Test(UT)
- Basic principle
- Decrypting reflected ultrasonic signals from any fault when ultrasonic pulses are introduced inside the test subject
- Subject and application
- Detecting any fault on the inside of a welded part, cast part, rolled part or forged part
- Features
-
- - High sensitivity to cracks
- - Capable of detecting any fault on the surface or inside
- - Great penetrability, automation available

Magnetic particle examination
- Basic principle
- Applying magnetic property to a ferromagnetic material such as steel triggers magnetic leakage field, and magnetic particles are stuck upon faulty areas when sprayed on the part
- Subject and application
- Detecting any fault on the surface or right under the surface of ferromagnetic material(welded part, cast steel or forged steel)
- Features
-
- - Applicable only to ferromagnetic material
- - Simple method and equipment
- - Not applicable to non-magnetic materials
- - Fast and cheap
- - Naked eye detection of a possible fault

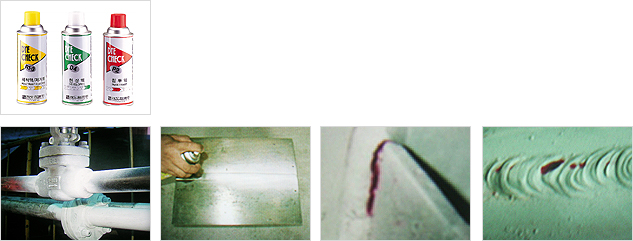
Penetrant Test (PT)
- Basic principle
- Test method of applying 3 test chemicals (penetrant, developer and cleanser) to identify the size, location and indication of the fault in order to detect a crack or a fault on the surface of the test subject.
A fault not existing under the surface cannot be detected, and suitable for conditions where the surface temperature of the subject is 15-50℃.
- Type of penetrant test
-
- Dye penetrant test: Dye penetrant test: Test flaw indication under natural light using red penetrant.
There are two types of penetrants: Solvent removable penetrant and water washable penetrant. - Fluorescence penetrant test : Fluorescence penetrant test: Test under UV ray at a dark location using fluorescence penetrant.
There are three types of penetrants: Post-emulsification penetrant, solvent removable penetrant and water washable penetrant.
- Dye penetrant test: Dye penetrant test: Test flaw indication under natural light using red penetrant.
- Features
-
- - Applicable to all types of material and part made of steel or non-steel.
- - Applicable to all types of material and part made of steel or non-steel.
- - Suitable for examining a heat processing crack, seam, overlapping forging, tear, glued status or welded part.
Leak Test(LT)
- Basic principle
- Detecting existence of a leak, its quantity and amount of leakage by introducing detection reagent such as ammonia, halogen or helium via pressure difference and the flow as well as by applying the detector on the surface of the test subject
- Subject and application
- Leakage detection on pressure container, oil storage tank or pipelines
- Features
-
- - Caution must be applied against toxicity and combustion of the detection reagent
- - Detection possible only for penetrated discontinuity
- - Small leakage may not be detected if volume of the test subject is too large
- - Mostly preferred for final integrity test

Eddy Current Test(ECT)
- Basic principle
- Detecting any fault by measuring changes of impedance of the test coil, or changes with eddy current caused by the fault of surface layer of the test subject
- Subject and application
- Detecting any fault on the surface or layer close to the surface of steel, non-steel pipe or wire, or measuring thickness of thin film, material identification
- Features
-
- - Non-contact detection
- - Fast detection, automatic detection
- - Excellent surface error detection capability
- - Detection of error with heat exchanger tubes
